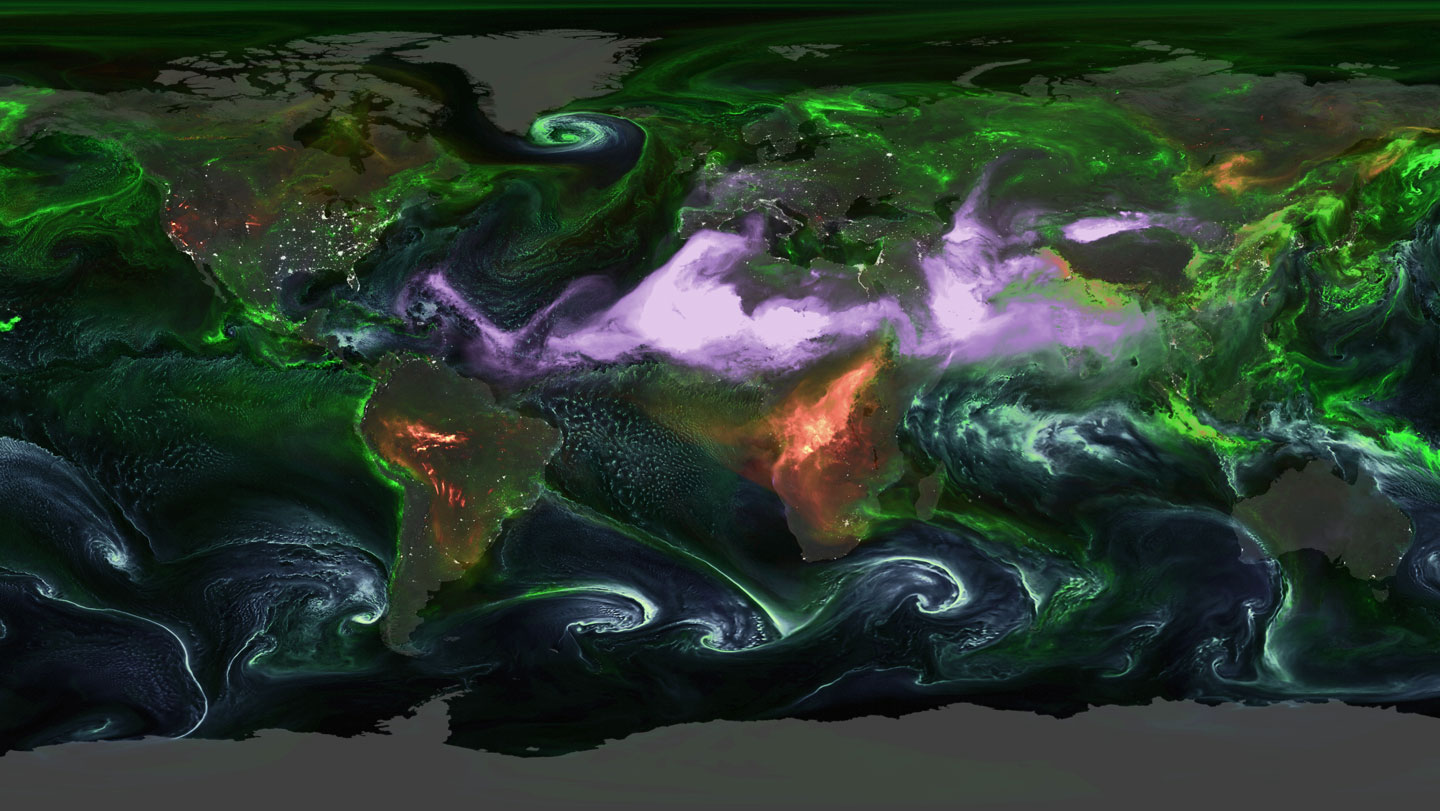
The sky abounds with aerosols, tiny particles with large sway over Earth’s temperature. A new NASA visualization reveals how these airborne particles swirl through the atmosphere.
The agency’s Goddard Earth Observing System tracks major aerosol types — sulfates, black carbon, dust and sea salt. It combines satellite and ground-based observations with advanced computer simulations to show how aerosols can affect air quality and visibility far from their sources. See where they loft in this visualization spanning August 1 to September 14, 2024.
Unlike greenhouse gases, which can persist for years and disperse globally, aerosols remain aloft for only days and form regional plumes. These high-flying motes counter climate warming by reflecting solar radiation back into space and acting as condensation nuclei, increasing the number of droplets in clouds and making the poofy masses more reflective.
“Those two effects together have offset about a third of climate warming … about a half a degree Celsius,” says atmospheric scientist Sarah Doherty of the University of Washington in Seattle.
Sulfates (green, in the visualization) are often linked to fossil fuel burning, especially coal. While some countries, including the United States, have curbed coal usage, many Asian nations rely on it, generating lots of sulfates. Volcanoes also spew sulfates; had the NASA visualization captured the 1991 eruption of Mount Pinatubo in the Philippines, Doherty says, the globe would have been blanketed in green.
The Sahara is the planet’s largest source of atmospheric dust (purple). Trade winds blow Saharan dust across the Atlantic Ocean, where it is thought to fertilize Earth’s largest rainforest — the Amazon. Some studies suggest Saharan dust may reduce Atlantic hurricane activity by stifling atmospheric moisture flow.
Unlike most aerosols, black carbon (red), which is emitted by biomass burning, absorbs solar radiation and warms the climate. Major sources include agricultural fires in sub-Saharan Africa as well as blazes in the Amazon and North America.
Sea salt (teal) is kicked up by wind and crashing waves, so its abundance is usually tied to wind speed, Doherty says. A lot of salt gets lofted over the Southern Ocean, where strong winds called the Roaring Forties race around the globe, unobstructed by landmasses.
As countries take steps to tackle air pollution, the cooling influence of aerosols is expected to fade. In fact, this may already be occurring. “We’ve seen a recent acceleration in the rate of warming,” Doherty says. “There are some analyses that are indicating that that’s at least in part attributable to the decline in aerosols.”